Users:General FEM Analysis/Elements Reference/Truss1
Contents |
General Description
Element Type
- This TRUSS1 element is a truss element with 3 translational degrees of freedom per node
- The truss element neglects bending and torsional stiffness
- The ratio of the cross-sectional dimensions and the length is much smaller than 1( a/L << 1 and b/L << 1), the truss is reduced to its center-line
- The cross-sectional area is constant over the element
- The truss element is also used as a cable, as which it can also account for prestress
Degrees of Freedom
The membrane element uses the 3 translatoric degrees of freedom, DISP_X, DISP_Y, DISP_Z.
Input Parameters
Parameter Description
| Compulsory Parameters | ||
| Parameter | Values, Default(*) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| MAT | EL-MAT int | Number for the used Material
e.g. MAT=EL-MAT 1 |
| AREA | cross-section area of the cable | |
| SIG11 | Prestress of the cable. | |
| Optional Parameters | ||
| Parameter | Values, Default(*) | Description |
| LAGRANGE | TOTAL, UPDATED | Definition of lagrange type. UPDATED for form finding and TOTAL for statics or dynamics. (e.g. LAGRANGE=UPDATED) |
Example of a Complete Input Block
EL-PROP 1 : TRUSS1 MAT= EL-MAT 1 AREA=1.0 PRESTRESS SIG11=1.0
Element Loading
Pressure
Pressure load -- characterized by its application in the current configuration, including direction and application area -- is implemented for the Membrane1 element. Note that it may also be included in the form-finding in order to define pressurized cushions, etc.
Dead Load
Dead load is implemented. It takes the thickness of the element and the density of the material which is then multiplied by the assigned acceleration value in the proposed direction.
Snow Load
Snow load is implemented. It considers the projected surface area of the element w.r.t. the load direction that is applied.
Theory
The theory and finite element formulation is described in detail in [1] , [2] and [3].
For the correct use of the membrane element and the interpretation of related results, the following aspects should be considered:
Material parameter
With the parameter MAT the material, that would be used in the calculation, for the membrane element is defined. The following materials are tested for the membrane element:
- linear elastic isotropic
- linear elastic orthotropic (Münsch-Reinhardt)
- multilinear elastic isotropic
- elastoplastic isotropic
- material on the basis of response functions
Thickness parameter
The parameter THICKNESS defines the thickness of the membrane. The thickness is assumed constant over the element.
Prestress directions on the surface
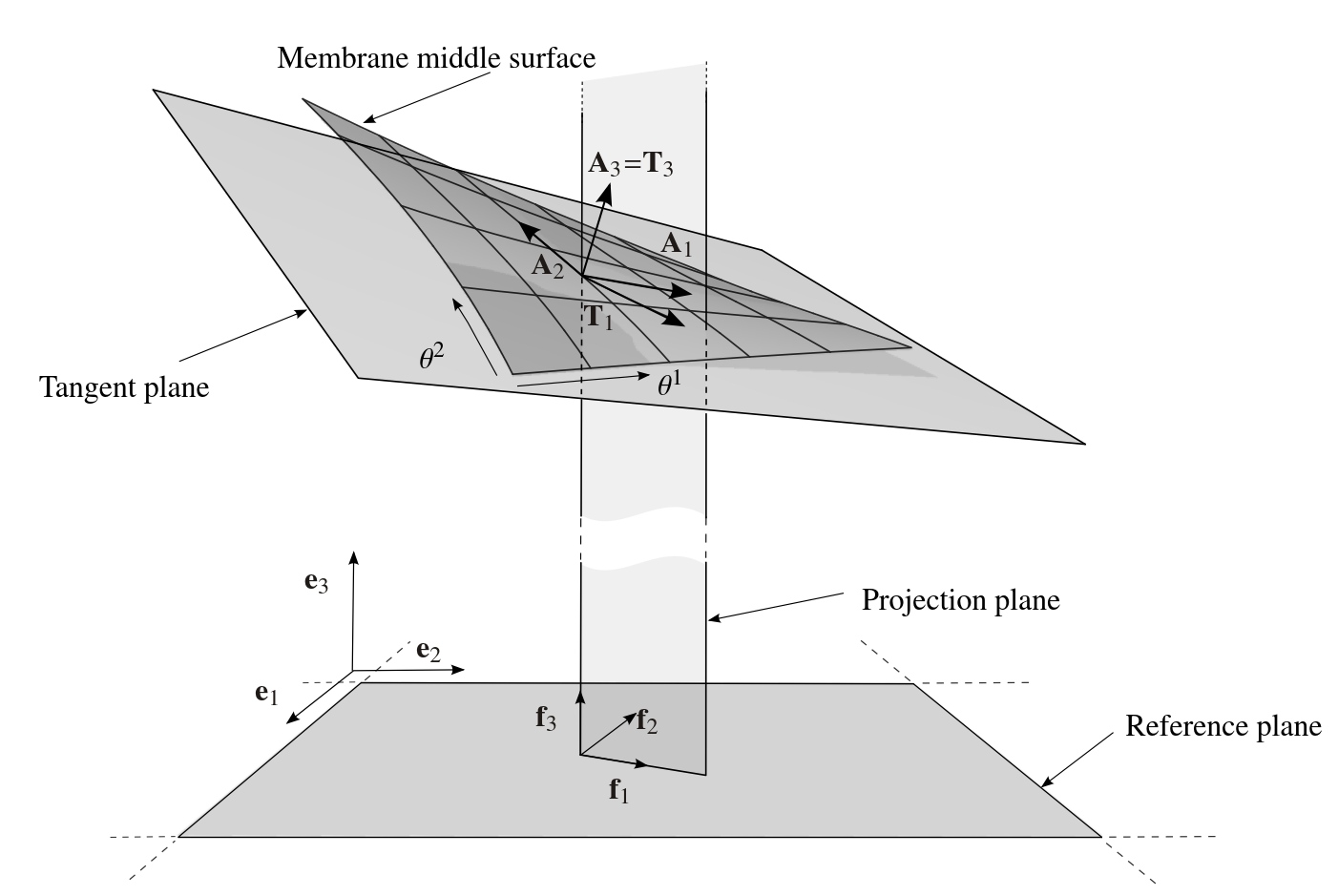
The parameters A_X, A_Y, A_Z and B_X, B_Y, B_Z are used to define the prestress directions on the surface, which is necessary in case of anisotropic prestress conditions. In this approach the principal directions of the prestress are defined in a plane area (see figure below). The definition of the area is given by the two vectors f1 and f2. The normal vector of the area can be calculated with the cross product of the in plane vectors f3=f1 x f2. Afterwards the line of intersection T1 of the area which is given by f1 and f3 and the curved surface can be calculated. In this approach T1 is interpreted as the first principal direction of the prestress on the curved surface. With the assumption that T3 is equal to the surface normal vector A3 (not normalized), the second direction of the prestress is calculated as T2=T1 x T3. W.r.t. the parameters for the input file, only the plane area with the vectors f1 and f2 has to be defined. Referring to the depicted approach the vector A defines the vector f1 and the vector B defines the vector f2.
Prestress state
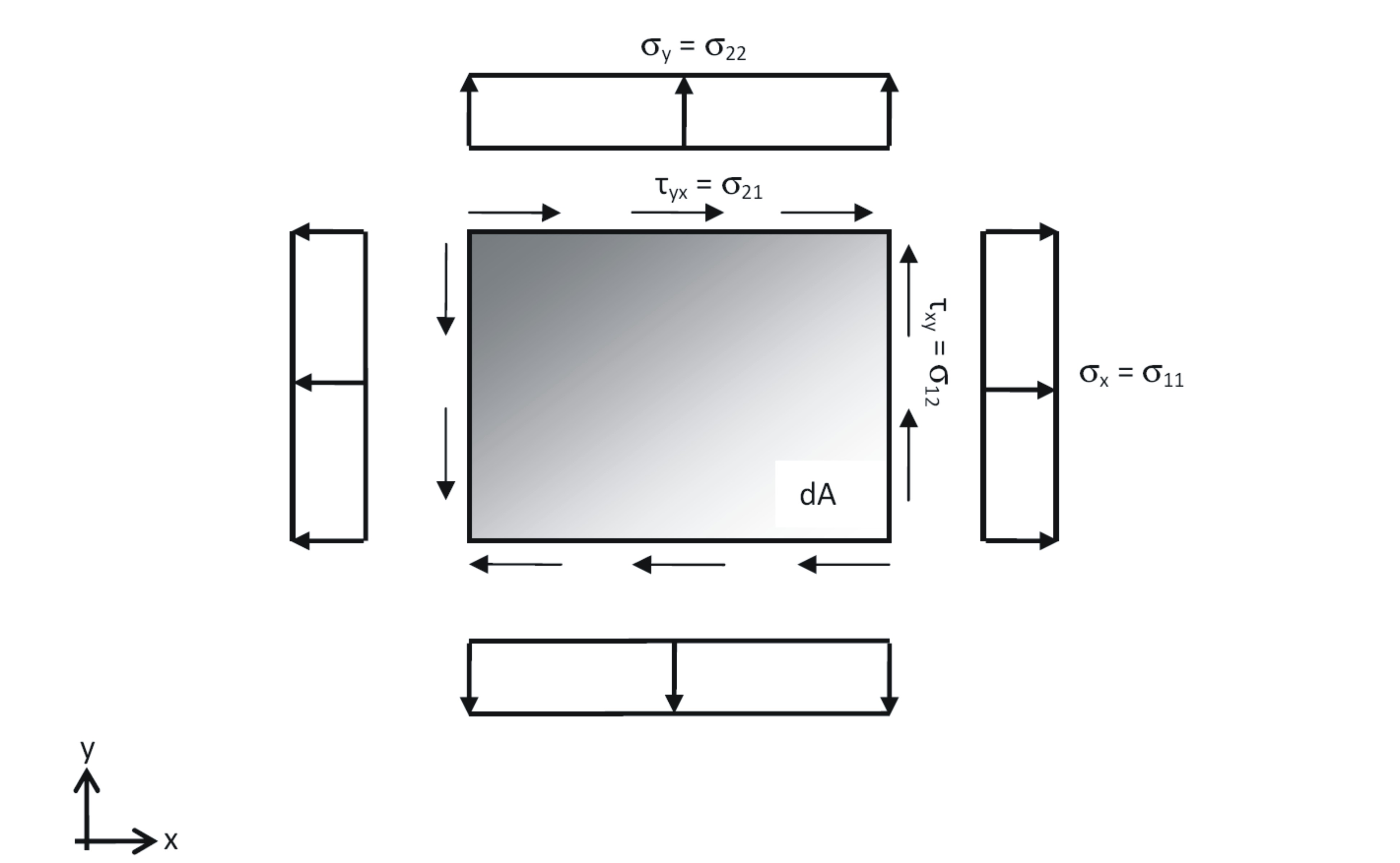
SIG11, SIG22, SIG12 describes the prestress of the membrane element. The element is based on the plane stress assumption. Due to that only normal and shear stresses in the midplane have to be defined. SIG11 is the stress acting in T1, SIG22 acting in T2 and SIG12 is the in-plane shear, whereas SIG12=SIG21 (see figure below).
Lagrange type
With the (optional) LARANGE parameter it is possible to switch between form finding and statical/dynamical analysis. For the value UPDATED the element is for form finding and for the value TOTAL the element is for statical/dynamical analysis. It is important that the LANGRANGE parameter match to the type of analysis.
References
- ↑ Dieringer, F.: Implementierung eines geometrisch nichtlinearen Membranelements in einer objektorientierten Programmierumgebung, Master's Thesis, Lehrstuhl für Statik, Technische Universität München, 2009
- ↑ Linhard, J.: Numerisch-mechanische Betrachtung des Entwurfsprozesses von Membrantragwerken, Lehrstuhl für Statik, Technische Universität München, 2009
- ↑ Dieringer, F.: Numerical Methods for the Design and Analysis of Tensile Structures, Lehrstuhl für Statik, Technische Universität München, 2014
| Whos here now: Members 0 Guests 0 Bots & Crawlers 1 |