Users:General FEM Analysis/Analyses Reference/Geodesic Lines
(→Example) |
(→Example of a Complete Input Block) |
||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
NUMGEO 1 NODE_I=293 NODE_J=732 | NUMGEO 1 NODE_I=293 NODE_J=732 | ||
NUMGEO 2 NODE_I=89 NODE_J=797 | NUMGEO 2 NODE_I=89 NODE_J=797 | ||
| + | NUMGEO 3 NODE_I=1 NODE_J=841 | ||
| + | NUMGEO 4 NODE_I=88 NODE_J=796 | ||
| + | NUMGEO 5 NODE_I=294 NODE_J=733 | ||
</pre> | </pre> | ||
Revision as of 14:04, 1 December 2016
Contents |
General Description
Geodesic line generation determines geodesic lines on a surface between two given nodes/points.
Structure of Equation System
A nonlinear problem is formulated by the equation r = f_int(u) where r specifies the residual vector and f_int defines the internal forces respectively. In general, the internal forces depend on the actual displacement field u. Thus, the equation is nonlinear with respect to the a priori unknown equilibrium displacements.
At the equilibrium point the residual vector is equal to zero. The above specified nonlinear problem is linearized for the actual displacement state and solved e.g. by a Newton-Raphson scheme where the residual vector is used to compute incremental displacements by K_t u_inc = r.
Input Parameters
Parameter Description
| Compulsory Parameters | ||
| Parameter | Values, Default(*) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| PC-ANALYSIS | int : FORMFINDING | Keyword of analysis with analysis ID |
| SOLVER | PC-SOLVER int | Linking to a linear solver (direct or iterative) |
| OUTPUT | PC-OUT int | Linking to output objects (specifies the type of output format, e.g. GiD) |
| COMPCASE | LD-COM int | Linking to computation case object which specify the boundary conditions (loading and supports). Only a single computation case is allowed. |
| DOMAIN | EL-DOMAIN int | Linking to the domain the analysis should work on |
| MAX_ITER_EQUILIBRIUM | int | Maximum number of equilibrium iterations that are allowed. |
| EQUILIBRIUM_ACCURACY | float | Equilibrium accuracy that has to be reached for convergence. The convergence is checked with the L2 norm of the incremental displacements. |
| FORMFINDING_ELEMENTS | PROP_ID int | The parts which should be included in the analysis, separation with comma. |
| FORMFINDING_STEP | int | Definition of number of formfinding steps. |
| GEODESIC_LINES | 0 or 1 | 0... FALSE. 1... TRUE |
| NUMGEO | int NODE_I = int NODE_J = int | Definition of start (NODE_I) and end (NODE_J) of geodesic line (nodes on the mesh) |
| Optional Parameters | ||
Example of a Complete Input Block
PC-ANALYSIS 1: FORMFINDING DOMAIN = EL-DOMAIN 1 OUTPUT = PC-OUT 1 SOLVER = PC-SOLVER 1 COMPCASE = LD-COM 1 FORMFINDING_STEP = 20 MAX_ITER_EQUILIBRIUM = 100 EQUILIBRIUM_ACCURACY = 1e-06 FORMFINDING_ELEMENTS = PROP_ID 101,201 GEODESIC_LINES=1 ! 0=FALSE 1=TRUE NUMGEO 1 NODE_I=293 NODE_J=732 NUMGEO 2 NODE_I=89 NODE_J=797 NUMGEO 3 NODE_I=1 NODE_J=841 NUMGEO 4 NODE_I=88 NODE_J=796 NUMGEO 5 NODE_I=294 NODE_J=733
Example
The following simple example shows the cutting pattern analysis of two parts from a four-point sail. It uses a static relaxation method, the flattening area is the mean surface normal and a Galerkin approach is used for the patterning method.
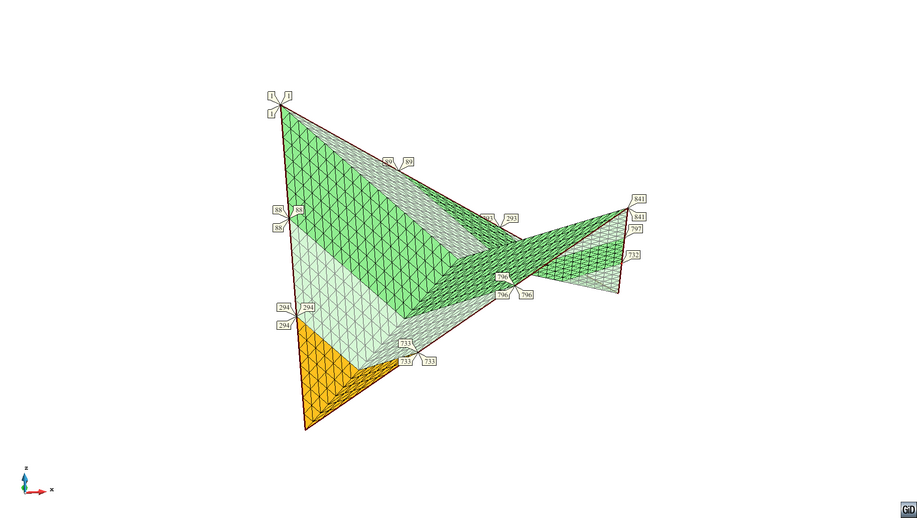
|
The cutting pattern of the two stripes is shown in the picture below.
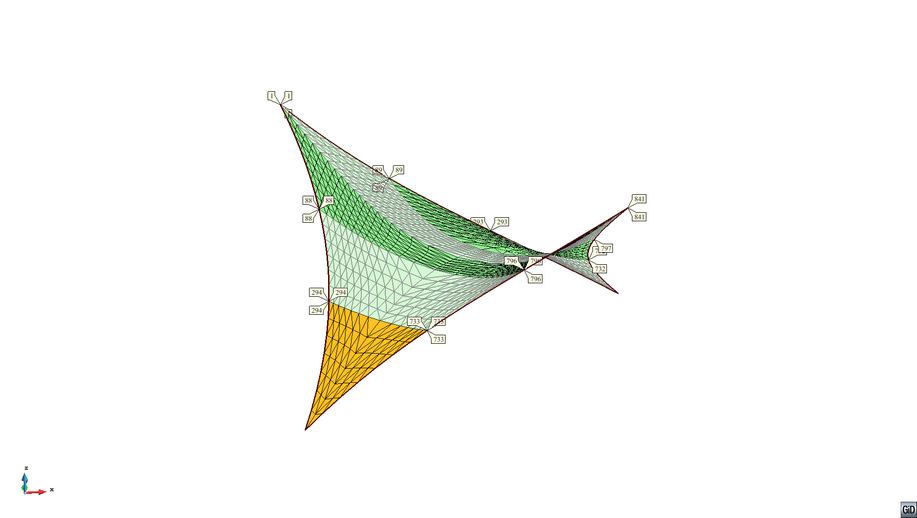
|
References
| Whos here now: Members 0 Guests 0 Bots & Crawlers 1 |