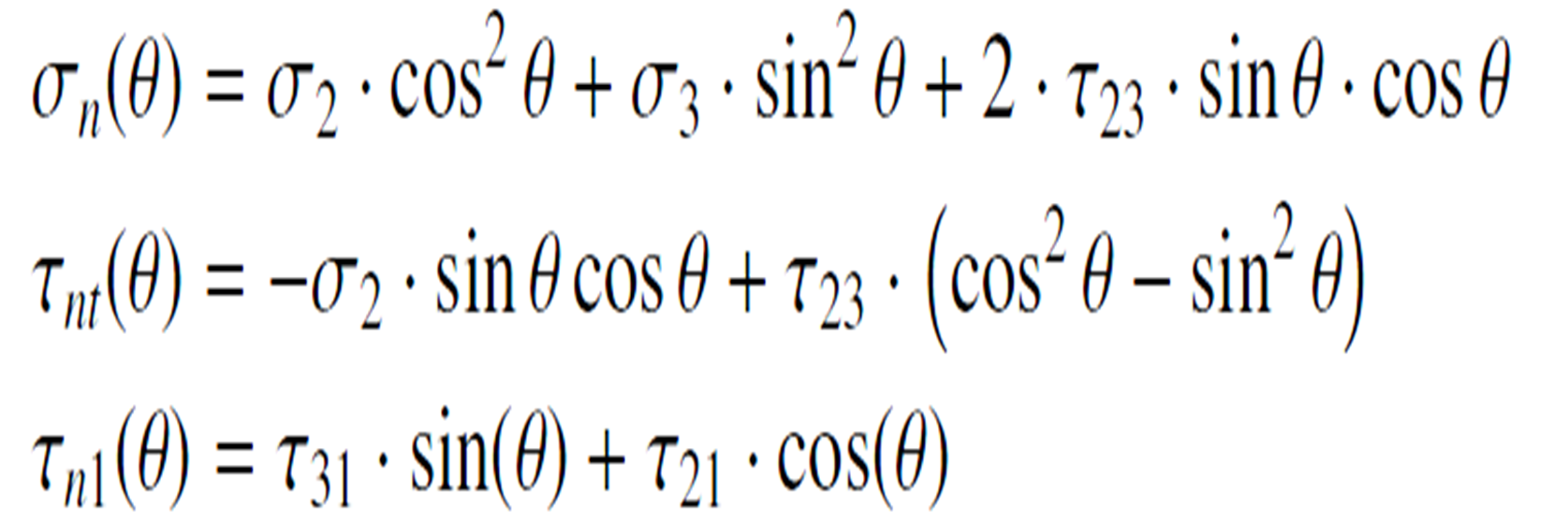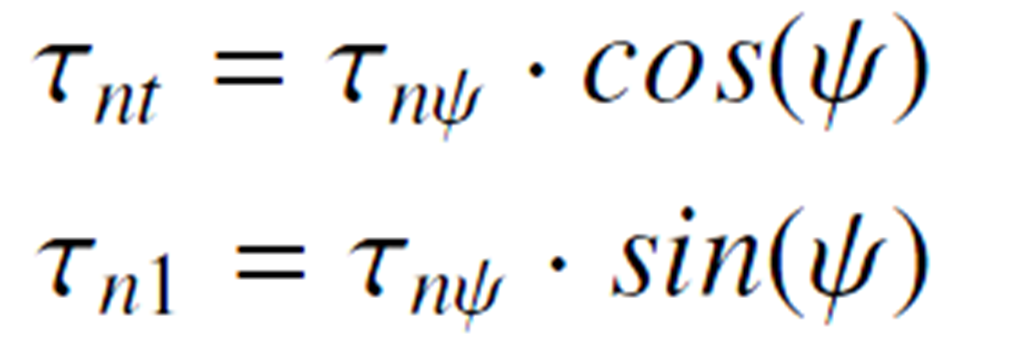Users:General FEM Analysis/Materials Reference/Puck Failure Criterion
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== General Description == | == General Description == | ||
| − | + | Puck Failure Criterion is based on Mohr‘s fracture hypothesis which is appropriate for brittle fracture behaviour of composite materials. It can distinguish between fibre fracture and different inter-fibre fracture. Both 2D and 3D formulations are implemented into Carat++. | |
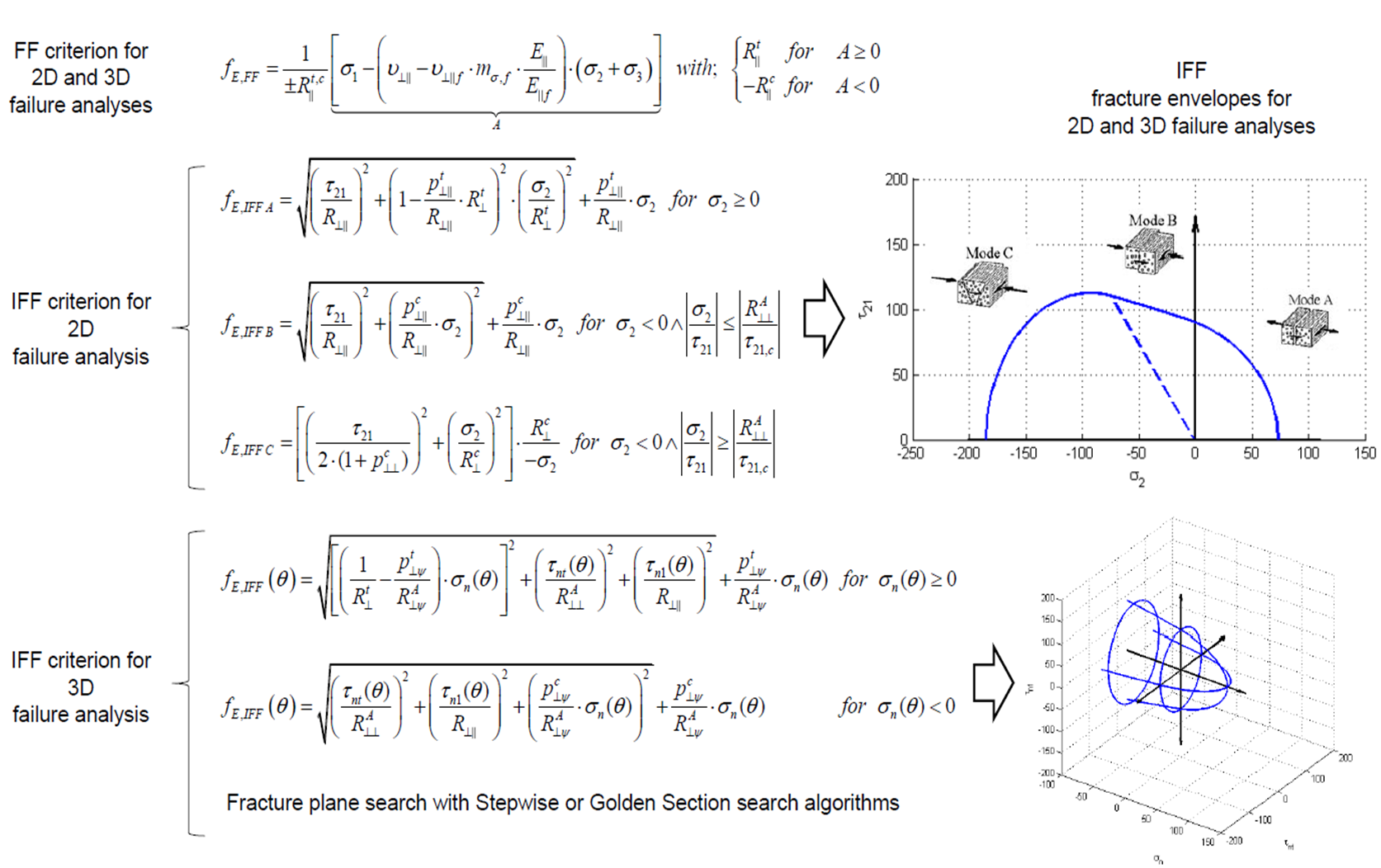
Available fracture modes for 2D Puck Criterion are: | Available fracture modes for 2D Puck Criterion are: | ||
* Fibre Fracture (FF) | * Fibre Fracture (FF) | ||
Revision as of 08:46, 15 February 2013
Contents |
General Description
Puck Failure Criterion is based on Mohr‘s fracture hypothesis which is appropriate for brittle fracture behaviour of composite materials. It can distinguish between fibre fracture and different inter-fibre fracture. Both 2D and 3D formulations are implemented into Carat++. Available fracture modes for 2D Puck Criterion are:
- Fibre Fracture (FF)
- Inter Fibre Fracture Mode A (IFF A)
- Inter Fibre Fracture Mode B (IFF B)
- Inter Fibre Fracture Mode C (IFF C)
Available fracture modes for 3D Puck Criterion are:
- Fibre Fracture (FF)
- Inter Fibre Fracture (IFF)
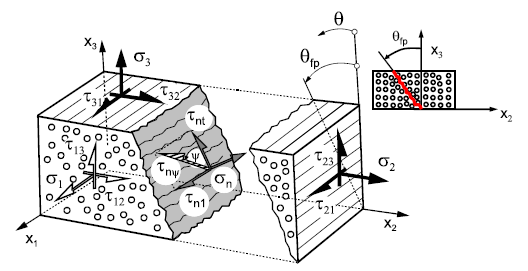
Stresses on the Fracture Plane
Strength Analysis
In order to judge if a stress vector on the stress spce is leading to damage, a mathematical expression is needed. This expression is called fracture condition an is written as the following general form:
Ri. : Strengths under corresponding stresses
F : Fracture function
There are 6 main strengths that should be related to the occurring stress state:
The general form of fracture condition can also be rewritten as following:
F < 1 : no fracture
F = 1 : fracture limit reached and fracture occurs
F > 1 : fracture limit exceeded
Parameter Description
Example of a Complete Input Block
| Whos here now: Members 0 Guests 0 Bots & Crawlers 1 |