Users:Structural Optimization/Response Functions/SurfaceCurvature
From Carat++ Public Wiki
(Difference between revisions)
(→Estimation of nodal curvature) |
(→Estimation of nodal curvature) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
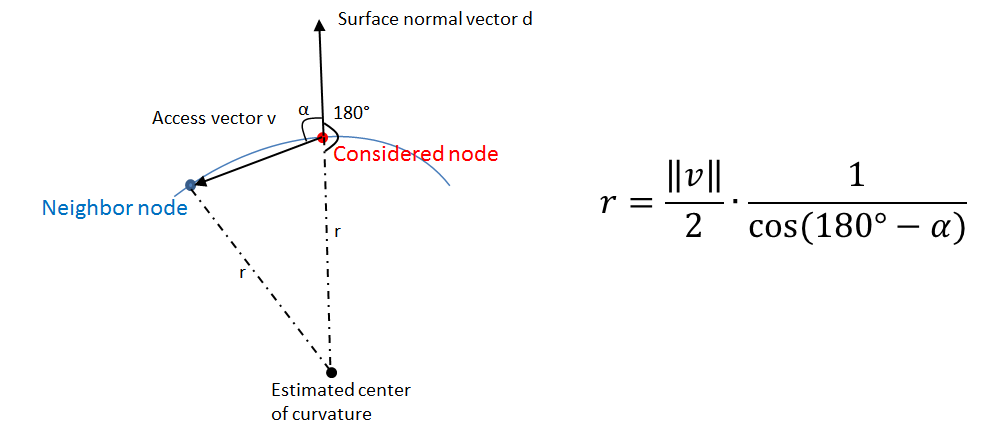
The nodal curvature is estimated using the surface normal vector and access vectors to the surrounding nodes. '''The estimation is based on a local spherical approximation of the geometry (see sketch below).''' So the radius of curvature r can be computed within the isosceles triangle. | The nodal curvature is estimated using the surface normal vector and access vectors to the surrounding nodes. '''The estimation is based on a local spherical approximation of the geometry (see sketch below).''' So the radius of curvature r can be computed within the isosceles triangle. | ||
| − | [[ File:curv_ks_sketch.png | | + | [[ File:curv_ks_sketch.png |500px | center |Sketch of curvature estimation in 1D ]] |
Revision as of 11:39, 21 April 2011
General Description
Short Info
In the field of structural optimization it is often necessary to apply a constraining of surface curvature in order to maintain manufacturing constraints. To this purpose, Carat++ provides an estimation tool to approximate the mean curvature at a surface node.
Estimation of nodal curvature
The nodal curvature is estimated using the surface normal vector and access vectors to the surrounding nodes. The estimation is based on a local spherical approximation of the geometry (see sketch below). So the radius of curvature r can be computed within the isosceles triangle.
| Whos here now: Members 0 Guests 0 Bots & Crawlers 1 |